Estimated read time: 6 minutes
What Is DNS Filtering?
DNS filtering or DNS blocking is a security measure that blocks users from accessing dangerous websites or malicious domains. DNS filtering is a common implementation in an organization’s security system, mitigating threats like phishing attacks and other web-based threats. DNS filtering services allow organizations to block access to suspicious websites and reduce the risk of malware penetrating the network.
What Is a Domain Name System (DNS)?
A domain name system translates a domain name such as Shieldoo™️ - Shieldoo secure network (mesh) and its outstanding features into a string of numbers – essentially, the internet protocol (IP) address. Devices capable of connecting to the Internet have respective IP addresses.
DNS saves users from memorizing long strings of numbers. Whenever a user visits a website, their device connects them to the right IP address to access the content of the requested domain name.
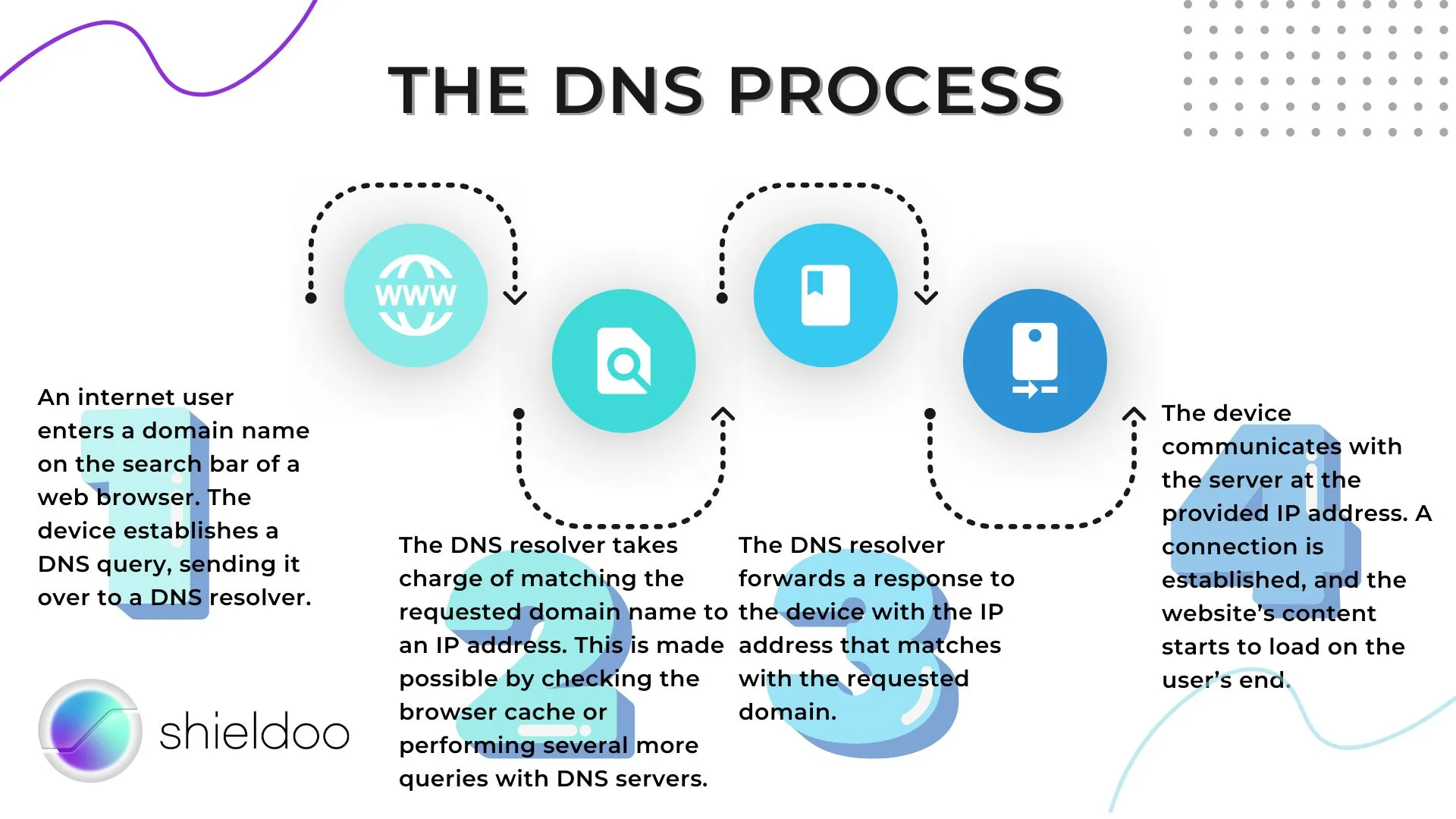
The DNS process
The DNS process involves the search for the right IP address for a device to load the website requested by the user. The steps to the DNS process are as follows:
- An internet user enters a domain name on the search bar of a web browser. The device establishes a DNS query, sending it over to a DNS resolver.
- The DNS resolver takes charge of matching the requested domain name to an IP address. This is made possible by checking the browser cache or performing several more queries with DNS servers.
- The DNS resolver forwards a response to the device with the IP address that matches with the requested domain.
- The device communicates with the server at the provided IP address. A connection is established, and the website’s content starts to load on the user’s end.
How Do DNS Filters Work?
DNS filtering services enable organizations to lay down permissions for the websites that business users may access. DNS web filtering sifts through website access permissions, with custom settings for organizations to prevent users from visiting malicious websites and other web threats.
DNS filtering services can assign DNS resolvers to filter domain queries and grant access according to a blocklist. A blocklist enumerates malicious websites identified by an organization to block employees from accessing these websites or inviting phishing attacks from harmful links.
Say, for instance, a well-disguised virus attack redirects an unknowing user to access a suspicious website. The employee’s device will begin with sending a query to the DNS resolver. The DNS resolver refers to the organization’s blocklist. If the website is included on the list, the access request will be blocked, stopping the website from loading its malicious content on the user’s device, impeding the barrage of attacks.

What Is DNS Filtering Used For?
DNS filtering oversees user access to websites through content-based filtering and blocking. Organizations equip their security architecture with DNS filtering for the following use cases:
Combat malware infection
Infecting a network with malware is among the potent online threats an organization faces. Malware is unsuspecting, and Internet users may come into contact with them through redirect links. Just clicking or navigating a malicious web page can lead to the installation of unwanted content on the organization’s computer system.
Malicious content can undo an organization’s years of hard work and breach sensitive client data. Hence, DNS filtering services are a crucial cybersecurity measure to block access to malicious websites and suspicious activity across the Internet.
Mitigate phishing attacks and exploits
Phishing attacks lure users into providing login credentials for a fake website that is an indistinguishable counterfeit of an otherwise established website. These phishing websites scam users to give up account details for sensitive assets such as their bank accounts, administrator access in the business network and more.
A DNS server, however, is capable of identifying fake and authentic websites by tracing their IP addresses. If the DNS resolver discovers a match on the blocklist, it will shut down any communication with the server at that IP address immediately, putting a stop to the phishing scam.
Meet compliance regulations
Organizations store sensitive client data online and in their local databases. Without preventive measures like a DNS filter, these data are prone to breaches, putting the clients’ safety and privacy in danger. DNS filtering upholds an organization’s compliance to the policies regarding client protection and data privacy.
Restrict prohibited content
Employee productivity plays a significant role in an organization’s growth and performance. To enhance productivity in the workplace, organizations can deploy DNS filtering to restrict access to recreational websites. Recreational websites like video-streaming platforms and online forums pose a high cybersecurity risk for the business network. Their lack of security certificates can introduce loopholes in the network, which hackers may exploit.
In addition, employees spend valuable office hours navigating such websites without any relation to their obligations at the office. Thus, organizations can make the decision to block user access for these websites. A common DNS filtering type used for such situations is time-based DNS filtering. Time-based DNS filtering enables an organization to schedule website restrictions around working hours. Such a technique dispels security threats, whilst enhancing employee efficiency in the workplace.

DNS Filtering vs URL Filtering
Web filtering is an umbrella term for technologies that filter user activity and oversee web traffic for web pages with suspected malicious content. Web filtering includes DNS filtering and URL filtering, among others.
DNS web filtering
DNS filtering blocks requests from websites whose domain names are blacklisted due to malicious and inappropriate content. DNS filtering secures a business environment from potential cyberattacks.
URL filtering
URL filtering, on the other hand, refers to filtering and blocking individual web pages. This web filtering type allows companies to control the amount and type of content business users can tap into on a business network. URL filtering refers to a data repository where URLs are specified by topic and their accessibility to employees.

Blacklist vs Whitelist
Blacklist
In cybersecurity, a blacklist, also known as a blocklist, is a listing of IP addresses without prohibited access. Websites often land on a company’s blocklist due to their infamous suspicious activities. Blacklisted domains may be exploiters of online scams, distributors of inappropriate content, or root causes for cyberslacking (i.e., social media, gaming platforms and online casinos).
Whitelist
Meanwhile, a whitelist is a database of domain names or IP addresses with authentic security certificates. Whitelisted IP addresses are trusted by the organization.
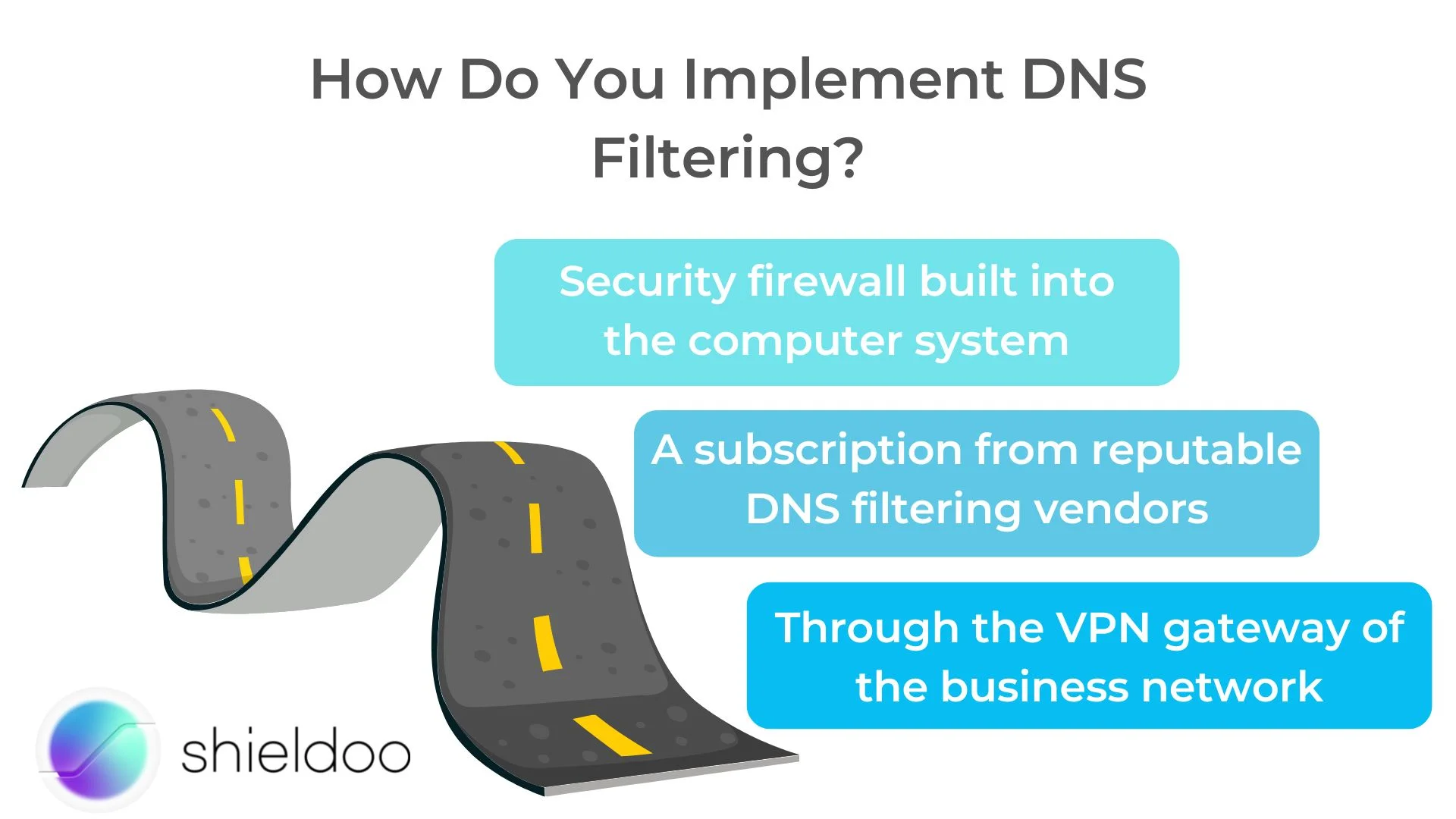
How Do You Implement DNS Filtering?
DNS filtering tools come in all sorts of security platforms available on the market. Every organization has preferences over the security architecture they deploy. In general, DNS filtering services can be carried out with the following:
- Security firewall built into the computer system
- A subscription from reputable DNS filtering vendors
- Through the VPN gateway of the business network
Is Shieldoo™️ a DNS Filter?
Shieldoo™️ is a secure mesh with peer-to-peer (P2P) connections, providing secure and private access to the business network, regardless of user location. It supports a plethora of security features, such as zero-trust network access (ZTNA), single sign-on (SSO) and multifactor authentication. However, it does not provide DNS filtering services.
FAQs
Why is DNS filtering important?
DNS filtering is a reliable security measure for enterprises with little to no budget for higher-end security solutions. DNS filtering blocks user access to websites that are harmful to the network or irrelevant to the tasks of employees.
How do I set a DNS filter?
A DNS filter may be set up as easily through a firewall. DNS filtering services are also available as a subscription plan or an access control feature of a bigger security solution.
What is DNS filtering in firewall?
A DNS firewall filters web traffic through endpoint services. DNS queries take place at the firewall, where a DNS resolver either grants access or blocks the IP address according to defined conditions.
What is web filtering?
Web filtering encompasses filtering and blocking methods on the Internet to restrict access or prohibit entry for specific users. Web filtering includes DNS filtering, content filtering, keyword filtering and URL filtering.
How does content filtering work?
Content filtering is often a component of firewalls, where specific patterns on content are taken into discretion. It determines whether the content, be it a string of text, image, or video, is unwanted or meets the conditions specified by an internet user or an organization to grant access.





