Estimated read time: 8 minutes
VPN vs SDP

Both are popular ways for businesses and individuals to protect their data from prying eyes. So, what's the difference between a Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Software Defined Perimeter (SDP)? Unfortunately, virtual private networks are becoming more and more insufficient for current security requirements. So, software defined perimeter goes ahead, and it seems like they can solve all of the vulnerabilities that arise from using a VPN.
VPN = VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORK
A virtual private network is a network connection based on secure virtual tunnels between points that protect users on public networks. Virtual private networks authenticate users outside the network before letting them in through the tunnel. If I use a VPN, my internet provider and third parties will not be able to monitor which websites I have visited or what data I am transmitting and receiving because the source of my data is becoming a VPN server. But regardless, VPNs have too many disadvantages.
DISADVANTAGES OF VPN
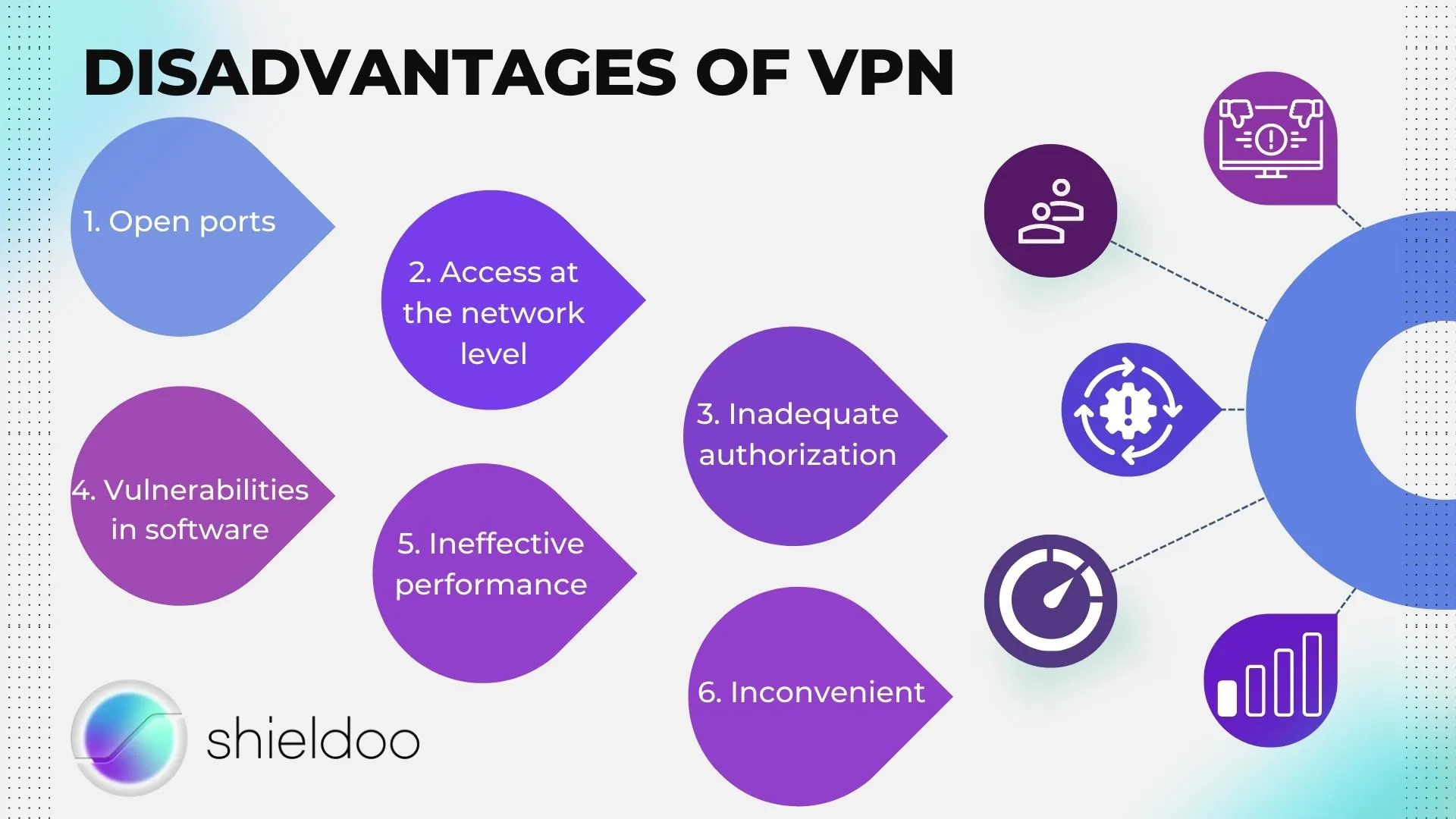
Open ports
An open port does not immediately indicate a security issue. However, it can provide an attacker with a path to an application listening on a given port. An attacker could exploit this, such as weak credentials, no two-factor user authentication, or even a vulnerability in the application itself.
Access at the network level
When VPNs authenticate users and allow them to enter the corporate network, they gain unrestricted remote access, exposing the entire network to threats. This flaw causes the company's data, applications, or intellectual property to be vulnerable to attack.
Inadequate authorization
Unlike SDP and zero trust networks, VPN does not require identification of the user or device attempting access to network resources. And because users often enter incorrect passwords and not to mention the millions of stolen user data available for sale on the dark web, hackers can intercept and obtain two-factor verification codes on online accounts.
Vulnerabilities in software
Hackers have attacked many popular VPN systems with software vulnerabilities over time. They look for the vulnerable VPN software, so it's essential to keep it updated.
Ineffective performance
VPNs can have latency issues because they use the computer's power to encrypt and route data across remote servers. Because of this, it may suffer from performance issues, including slow applications and outages.
Inconvenient
Setting up a VPN is a costly and time-consuming process that requires a lot of effort from the security team and remote workers. In addition, VPNs are not a secure network solution due to typical technological vulnerabilities.
SDP = SOFTWARE DEFINED PERIMETER
Software Defined Perimeter is a way to hide infrastructure connected to the Internet (servers, virtual machines, etc.) so that external parties and attackers cannot see it, whether it is deployed locally or in the cloud. The goal of the software defined perimeters approach is to establish a network based on software, not hardware. So, for example, a company using the SDP protocol is invisible on its servers and other infrastructure so that no one can see it from the outside. At the same time, authorized users still have secure access to network resources.
BASIC PRINCIPLE OF software defined perimeter
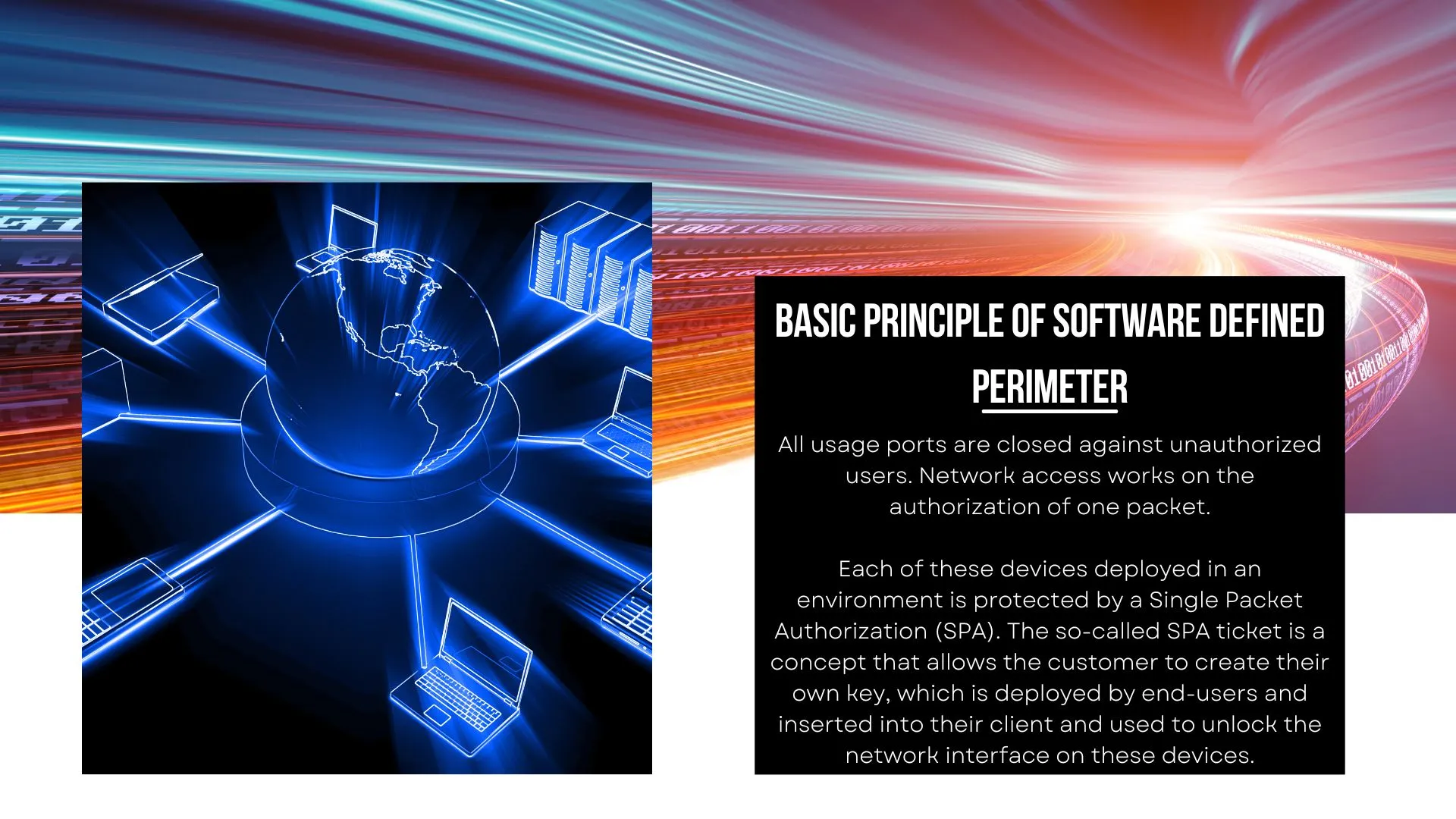
All usage ports are closed against unauthorized users. Network access works on the authorization of one packet.
Each of these devices deployed in an environment is protected by a Single Packet Authorization (SPA). The so-called SPA ticket is a concept that allows the customer to create their own key, which is deployed by end-users and inserted into their client and used to unlock the network interface on these devices.
The end-user starts communicating with the device by sending a SPA token. The SPA token is analyzed to ensure that it is the correct, the still valid token that comes from the device or the same device that sends it during transmission. There is no MITM (Man in the middle), and the token is verified for editing in any way. If the user does not have a token or is an unknown, unauthorized user without a token, the device will completely ignore all attempts to communicate with him.
There are no open ports connected to the device unless you have a SPA key.
Comparison of SDP vs VPN

Ports
VPN authentication protocols require open ports exposed to the Internet, which provides attackers with information about the services behind the Perimeter and the target of the attack. Authentication must take place before any services are discovered. There are no open ports connected to the device when using software defined perimeters unless you have a SPA key.
Costs
The overall cost of VPNs is rising rapidly. Different firewall VPN devices (whether virtual or physical) can be expensive, and both the number of data centers and cloud instances and remote users increase the cost. Businesses, therefore, need to purchase additional scaling and support capacity. However, the most significant hidden price for VPN is the time for technical support for IT end users/support - covering VPN setup and configuration, as well as ongoing troubleshooting. On the other hand, SDP can scale immediately when demand increases without additional servers or software. SDP cloud deployment can be extended to many users without requiring additional investment. The SDP client is easy to install and can be installed separately without IT support.
The target for hackers
Although VPN contains some security features since it is already an older technology, it can no longer respond effectively to security risks in many cases. SDP protects companies from a wide range of threats and pirate techniques that attackers use on the network.
Reports
VPN does not provide any reports and network monitoring, but SDP does. These reports can be used for network diagnostics and overall condition, and last but not least for audit.
Latency
There are several reasons why VPN latency is worse. For example, the distance of the server, if the user connects from India, for example, and the VPN gateway is located in NY, then due to the distance, the request must travel a long distance, and there will be time delays. Another problem may be encryption because the data must be encrypted and decrypted when passing through a VPN gateway. Other may be the server's capacity or how many people use the VPN, which will also affect performance. SDP does not rely on devices, so it does not suffer from such limitations. It can scale very well in line with demand but at the same time offer a consistent level of service. Instead of directing users back to the data center, they are redirected to the nearest location, and thus the latency compared to VPN is reduced there.

ZTNA = ZERO TRUST NETWORK ACCESS
ZTNA (Definition of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) - Gartner Information Technology Glossary) is also known as a Software Defined Perimeter (SDP). Still, more than software, it is a set of features that allow remote users to access internal applications securely. As a result, zero trust networks provide remote users with a seamless, secure network connection to private network resources without posting applications to the Internet or placing them on a network.
SDPs use the standard principles of a zero-trust architecture, which means that access is denied until the user can prove their identity. In addition, SDPs use a driver that collects various data, such as the device's operating system, Wi-Fi device location, an application used, and so on.
Real-time data is used to create a risk for each request, depending on the user's access to the resource. With these tools, it is easy for an IT or a security team to customize and automate user access (access management) based on the role and needs of the individual within the organization. As a result, sensitive or privileged data can be kept secure. At the same time, access to data and applications remains invisible, regardless of their location.

Final words
With the increase in cyber threat attacks across both private and public networks, it is more important than ever for businesses to generally protect themselves with features of Software defined perimeter and Zero trust networks. A traditional VPN can provide some protection but often has vulnerabilities that SDP does not have. So SDP is the new way to protect your data!
Try Shieldoo™️
Cyber security is becoming more and more important, which is why we provide you with essential information in a wide variety of articles on our blog. We also developed a new tool Shieldoo™️ based on Nebula from Slack which can help you to provide secure connection between end-users and servers. You can try your own private network here.
FAQs
Is SDP a VPN?
An SDP is an entirely different security solution from a virtual private network (VPN). VPNs earned a legacy for becoming an essential tool in establishing network security. However, as the Internet matures and threats to security increase, the limited features of a VPN are incapable of protecting sensitive data.An SDP is built on the Zero Trust principles, wherein no one inside or outside the network is trusted. Verification checks are performed before a user’s access request gets granted. SDPs reduce the risk of malicious activity by only granting minimal access to the application or data requested by the user.SDP overshadows VPN in terms of not only tighter security but also scalability. For VPNs to secure bigger networks, investing in more hardware is a must. SDPs on the other hand, enjoy flexible scaling across peer-to-peer and hybrid networks.
Is ZTNA and SDP the same?
An SDP is an entirely different security solution from a virtual private network (VPN). VPNs earned a legacy for becoming an essential tool in establishing network security. However, as the Internet matures and threats to security increase, the limited features of a VPN are incapable of protecting sensitive data.An SDP is built on the Zero Trust principles, wherein no one inside or outside the network is trusted. Verification checks are performed before a user’s access request gets granted. SDPs reduce the risk of malicious activity by only granting minimal access to the application or data requested by the user.SDP overshadows VPN in terms of not only tighter security but also scalability. For VPNs to secure bigger networks, investing in more hardware is a must. SDPs on the other hand, enjoy flexible scaling across peer-to-peer and hybrid networks.
Is Zero Trust a VPN?
The Zero Trust Security Model is a philosophy that trusts no user or device requesting access to an application. Solutions such as SDPs execute the principles of Zero Trust in user-device verification, namely, identity, context, and security posture.Thus, Zero Trust is not similar to a virtual private network. VPNs are a security solution where physical networks are protected from external malicious activities.
What is Cloud security alliance?
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) is a non-profit organization established in 2008, educating individuals and corporations about cloud computing and security. CSA actively engages in research to enrich the understanding of cloud security.
Do you need SDP or Zero Trust?
As mentioned before, SDP is the IT security solution that carries out the principles of the Zero Trust Security Model. Multi-factor authorization, single sign-on, and the like are just some of the verification features an SDP performs to protect and secure applications. Adopting the Zero Trust philosophy through software-defined solutions is an excellent strategy to protect business networks from malicious intent and the public’s eye.
Is VPN outdated?
With advanced IT solutions like SDPs breaking into the market, VPNs are slowly becoming outdated technology. VPNs fall short in adapting to the hybrid workspaces of today, decreasing security levels significantly. Due to VPNs operating from a physical network of computers, their coverage is limited and unable to offer security for employees accessing the network from home or outside the office space.





