Estimated read time: 7 minutes
In the mid-16th to 19th centuries, forts replaced towers with flanked structures known as bastions to fortify defense against ranged attacks. With the bastion host, the modern information age adopts the function of bastion forts to increase resistance against malicious attacks on computer systems.
In an article from 1990, cybersecurity researcher Michael J. Ranum first mentioned the idea of a bastion host. While elaborating on network firewalls, Ranum described that a bastion host is acritical structure, alongside firewalls, in upholding network security. Bastion hosts may be modified to reinforce its security measures and keep external threats at bay.
The bastion host has seen its heyday, but how does it fare in the current demands of enterprise networking? As technology advances at lightning speed, are bastion hosts still reliable? In this article, we’ll discuss how a bastion host works, its security risks, and the online security alternatives to a bastion server.
What is a Bastion Host?

A bastion host is a computer specially designed to mitigate cyberattacks and manage access rights to an internal network. Only authorized users may be granted access to the intranet. A bastion host is the only exposed point of communication; it sits outside the security firewall or operates from a demilitarized zone (DMZ). Users connecting to a private network from the public internet may only interact with the bastion host.
A bastion host is also called a jump box or jump server—a network system keeping track of all devices in a security zone. Bastion hosts run minimal services, often only operating a single application to restrict their attack surface to a minimum.
Types of Bastion Hosts
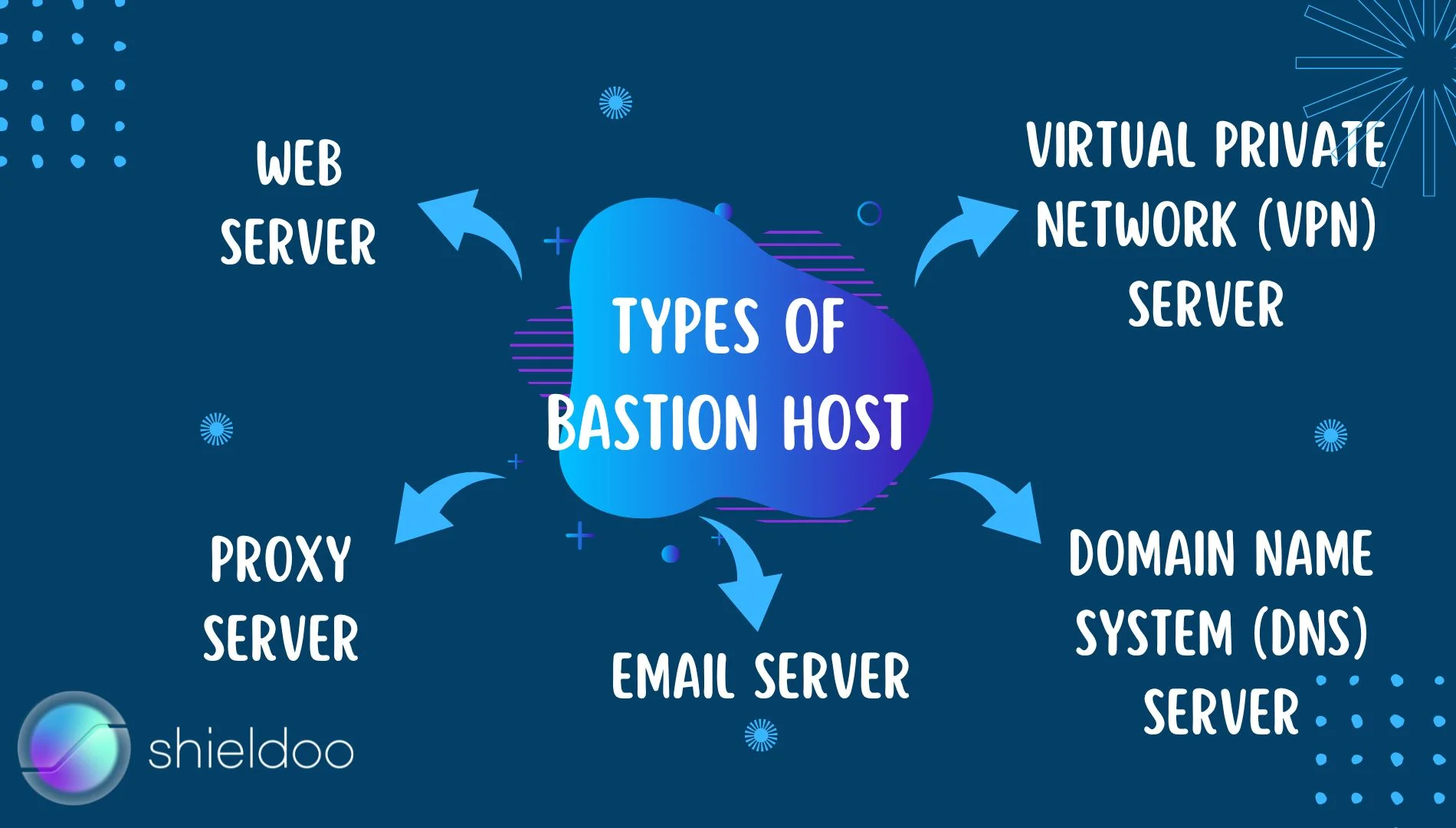
Bastion hosts are any single-application server or protocol providing perimeter access control security. These include:
- Web server
- Proxy server
- Email server
- Domain name system (DNS) server
- Virtual private network(VPN) server
How is a Bastion Host Used?
A bastion host is a strong security point in a private network. Most bastions are constructed to manage secure shell (SSH) services, monitoring communication and data exchange between computers. Network administrators can configure bastion hosts to sift through external traffic. While the bastion host manages network access, administrators can focus on reinforcing security measures in other aspects of the internal network.
A bastion host also allows for ease and convenience in user management. Upon leaving the organization, the employee’s access to company assets and other resources in private networks and the subnet are automatically revoked by the bastion host.
How does a Bastion Host Work?
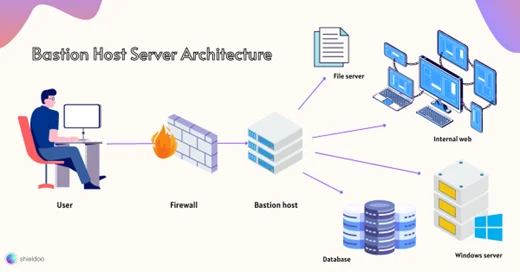
A bastion host is the entry point for systems and applications stored in a private network or intranet. When administrators and other users wish to access the intranet from an external network like the public internet, security risks like data loss and exposure are highly likely.
From the IT perspective, allocating multiple communication ports for the external network is not only dangerous but also impractical. Network administrators will have a hard time managing user traffic across all ports while maintaining asset security.
Thus, a bastion host comes in handy to bridge the gap between the internal network and the public internet. As an SSH proxy server, the bastion host’s sole purpose is to approve or deny communication requests. Functions, ports, user accounts, protocols, and applications unrelated to SSH proxy services are promptly disabled.
Bastion hosts only provide access to SSH connections from internal IP addresses. Administrators may grant access to an IP address whitelisted by the IT security team. As all connections are filtered through the bastion host, business users are not exempt from establishing SSH connections. To authenticate user identity, the bastion host requires SSH keys. Only then will users gain access to an asset or application stored in the internal network. User accounts in the intranet are assigned with SSH keys to access resources in the network or from its own subnet.
Additionally, bastion hosts keep track of network activity to alert administrators of any suspicious activity. The bastion host secures copies of system logs on a local machine for backup and recovery purposes. A filtering router may also be incorporated to support the bastion host in verifying data packets travelling between the public internet and the internal network.
What is the Significance of Bastion Host Servers in Cloud Computing?

Organizations use bastion hosts to reinforce intranet security amid threats and malicious individuals on the public internet. The rise of cloud computing has also led to a myriad of security risks; a bastion host is among the many cybersecurity measures to filter network activity and reinforce online security.
For instance, many organizations are embracing cloud-based services to accommodate remote work or hybrid office environments. Business users store data on the cloud through a virtual private cloud (VPC) for easy archival and retrieval. However, just like any virtual network, a virtual private cloud is vulnerable to external threats.
Remote business users will rely on public internet access to establish a connection with the internal network. A bastion host filters connection requests according to the user’s IP address. SSH keys will be required for further authentication, and only then shall a user connect to the intranet and gain access to its private resources.
The Best Practices of Securing Bastion Hosts

The main purpose of a bastion host is to withstand attacks and protect internal networks from security vulnerabilities and other threats posed by malicious entities on the internet. It is placed on the public side of the DMZ, filtering and channeling network activity and user traffic. As a critical security point in private networks, securing bastion hosts is best accomplished with the following practices:
1. Increase damage resistance of the bastion host.
The smaller the attack surface, the better. Dispose of functions that are not necessary for the bastion host to perform its duties.
2. Limit network access.
A bastion server shall only be accessible by authorized users. Administrators may restrict incoming traffic to the bastion; the filtering router shall filter through the corresponding IP address of every connection request and provide them with limited access to the network’s systems and applications.
3. Reinforce SSH protocol.
Despite assigning SSH keys, compromised accounts are still prevalent. Prevent this by adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard SSH keys and prevent unauthorized entities from accessing the internal network. Regular audits on the status of SSH keys enable administrators to determine the status of compromised and orphaned keys.
Security Risks of Bastion Hosts

Though bastion hosts still serve their purpose to defend private networks from external attacks, it is undeniable that it is an archaic security technology. As modern computing becomes more decentralized, a single-purpose bastion server may put internal networks at greater risk.
Bastion Hosts are Publicly Visible
A bastion host provides added resistance to cyberattacks, as it is specifically designed to counter cyberattacks through a reduced threat surface. However, because bastion hosts are visible to the public, cybercriminals can use more damaging attacks to infiltrate private computer systems.
SSH is an Outdated Computing Solution
SSH has not evolved to keep up with the current demands in enterprise networking and security. Key management, for instance, has not scaled for centralized management. SSH does not support integration for other security measures, making it difficult to authenticate orphaned and unused keys.
SSH Keys Grant High-Level Network Access
Once a cyber attacker gets hold of an SSH key, they gain full control of the entire computer network. The bastion host is deemed useless, as the cyber attackers can bypass security points and exfiltrate critical data upon entry.
The Azure Bastion Host
The Azure Bastion service allows a user to connect to a virtual machine from the Microsoft Azure portal. Another method to connect is through the remote desktop protocol (RDP) client or the native SSH protocol pre-installed on the local computer. Azure Bastion keeps RDP or SSH ports from being exposed to the public internet. Additionally, virtual machines do not require an IP address to operate.
Alternatives to a Bastion Host Server
Organizations expose themselves to cyber threats by simply relying on archaic security technology. The bastion host, just like RDP, SSH, and VPN can no longer withstand the complexities of today’s remote computer networks. As more system files and resources are stored on the cloud, security systems have to be deployed across various devices for maximum protection.
Modern-day cybersecurity is geared towards increasing the security of every resource stored on the network, rather than protecting entire networks. Zero trust network access (ZTNA) is an excellent security model wherein every access request is treated with the least trust, regardless of user role or proximity to the network infrastructure.
For every access request, a user has to verify their identity and motive in accessing a resource. Upon validating login credentials, the user is granted the lowest privilege access—that is, they may only navigate the network at a minimum level to accomplish their tasks. For every new system file or piece of data they require, the user has to undergo the same cycle of identity authentication to proceed.
Shieldoo™️ secure network (mesh) is a reliable alternative to archaic bastion hosts. It is a scalable cloud-based security software based on Nebula from Slack. Following the principles of zero-trust, Shieldoo™️ enables ZTNA technology to protect user traffic and user credentials from unauthorized third-party services.
To reinforce security across multiple devices, Shieldoo™️ offers a plethora of security measures such as single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication. Peer-to-peer connections ensure lightning-fast data transfer and encrypted user activity across the Internet.
Elevate Business Security Structure with Shieldoo™️

As cybercrimes grow more complex by the day, a bastion host may not be able to hold its ground against brute attacks. Bolster cybersecurity wherever and whenever with cloud-based security tools such as Shieldoo™️ to protect critical resources and applications from the dangers of the public internet.
Try Shieldoo™️
Cyber security is becoming more and more important, which is why we provide you with essential information in a wide variety of articles on our blog. We also developed a new tool Shieldoo™️ based on Nebula from Slack which can help you to provide secure connection between end-users and servers. You can try your own private network here.
FAQs
Is a bastion host network a firewall?
As a bastion host refers to any system or protocol equipped with a secure perimeter, a bastion host may be a firewall. Bastion hosts often work side-by-side with security firewalls to filter network traffic.
How are bastion hosts similar to jump servers?
A jump server refers to a network that manages devices in a different security zone. Often, bastion hosts are described as jump servers as they manage traffic and user access on the intranet from the demilitarized zone (DMZ).
Why is a bastion host located in the external network?
A bastion host is an external-facing server; it is the only port of a private network exposed to the public side of the internet. It sits between the intranet and the public internet to restrict user access and resist any potential attack.





