Estimated read time: 7 minutes

What Is BYOD?
BYOD, short for Bring Your Own Device, refers to the practice of employees using personal devices in the workplace to access corporate networks and critical assets. Personal devices range from laptops, smartphones, tablets, USB drives, and more.
With the shift in work environment since the COVID-19 pandemic, BYOD is quickly becoming the new normal. Working remotely is more manageable as employees can simply use their own devices to accomplish work. More companies are also embracing BYOD as a cost-effective alternative to providing company-issued devices. Instead of buying new computers, the company can reallocate resources to optimize other pressing matters such as project management and IT operations.
BYOD Security: How Significant Is It?
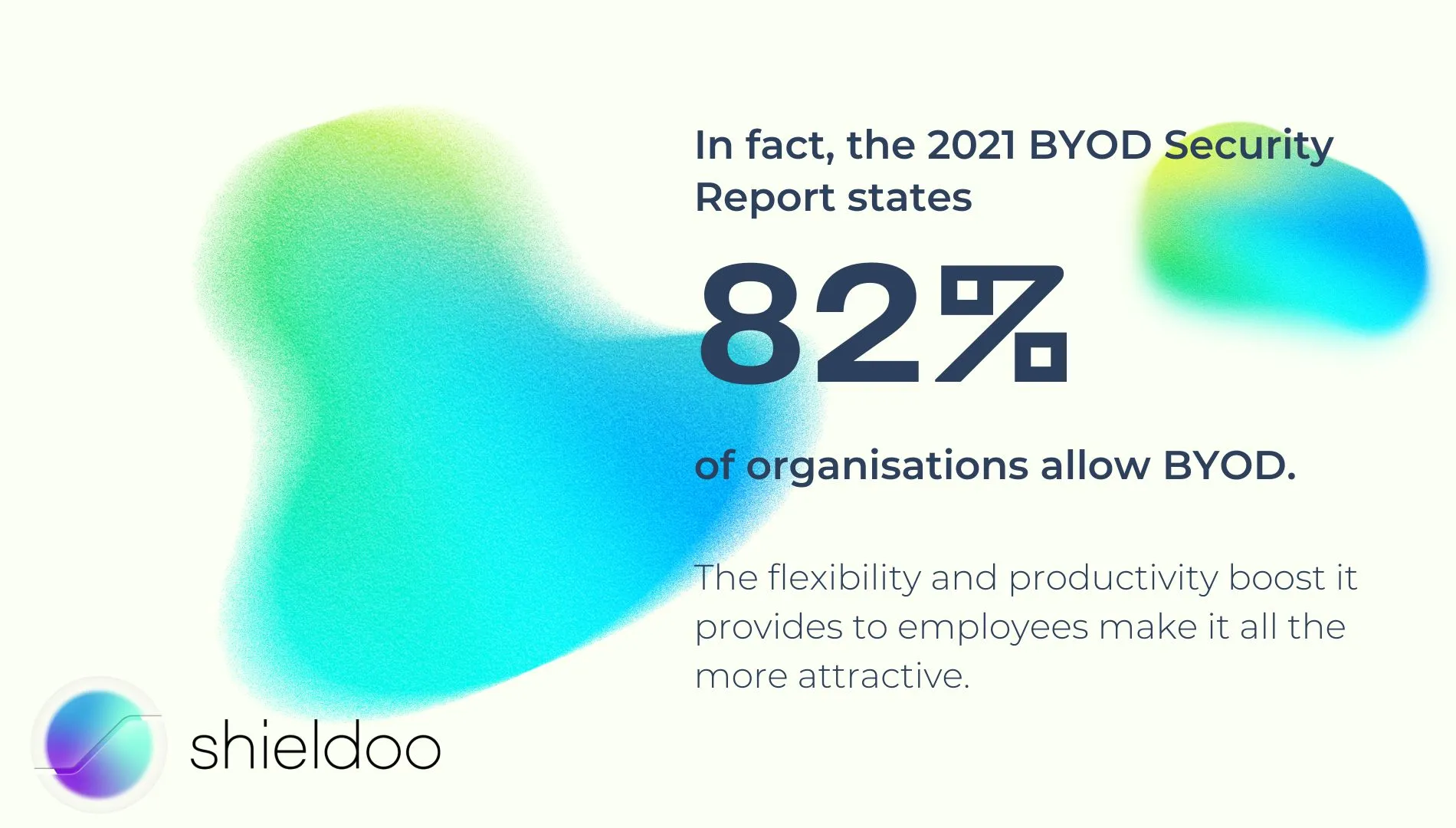
The early 2010s saw an increase in practicing BYOD in corporate environments. Today, it is gaining newfound recognition as more employees are working outside the office. In fact, the 2021 BYOD Security Report states 82% of organizations allow BYOD. The flexibility and productivity boost it provides to employees make it all the more attractive.
However, this practice leaves business networks vulnerable to security risks. BYOD security is a must in safeguarding company data from cyberattacks and malware.
Personal devices are comfortable to work with but are not always the most secure for handling business transactions and other sensitive data. BYOD security ensures policies are in place to mitigate data breaches.
What Is a BYOD Security Policy?
Corporate devices were the norm until laptops, smartphones, and tablets became indispensable tools for almost every employee. Personal devices are not fine-tuned to a company’s digital security standards in safeguarding corporate data and business transactions. Without proper policies in place, BYOD raises the risk of data loss and leakage, among others.
The shift in technology and business practice makes it almost inevitable for employees to access work-related matters on their personal devices. A BYOD security policy helps mitigate the risks and vulnerabilities the company and its employees may encounter while using personal devices and other equipment.
The Benefits of a BYOD Security Policy
There’s more to BYOD than the comfort it brings to employees when working with devices they’re accustomed to. In fact, the BYOD market is projected to reach $157.3 billion by 2026. Hybrid workplace arrangements, cost-effectiveness, and operating system optimization are just several factors emphasizing the advantages of a BYOD security policy.
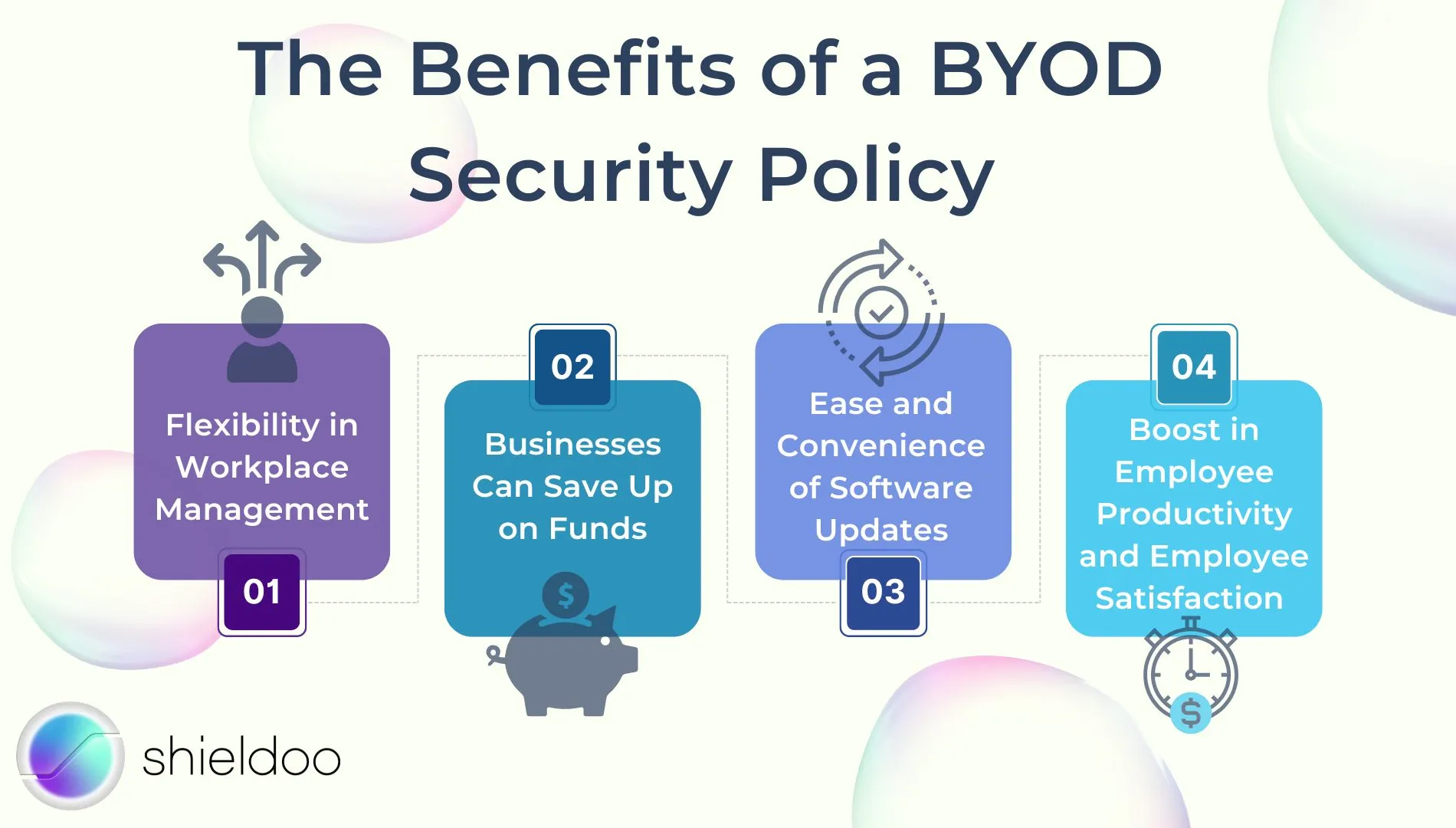
Flexibility in Workplace Management
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted how work is no longer limited to office grounds. As more people begin to embrace the convenience of remote work, personal computers and mobile devices saw an increase in usage rate. On average, employees use 2.5 devices at work, with 14.4% of employees using personal devices to accomplish tasks. As such, employees aren’t limited to company-issued equipment and accomplish work whenever and wherever they are.
Businesses Can Save Up on Funds
With a BYOD policy in place, companies can save significant money. Enterprise computers are expensive, and often go out of date within five years. Purchasing a device for every employee and allocating a budget for repair and replacement are quite difficult to manage, especially for startups. Not to mention, employees are more likely to stay up to date with the best devices and technology to help them get the work done.
Ease and Convenience of Software Updates
Often, IT departments will be flooded with requests from employees to upgrade program software or operating systems. This adds an unnecessary burden to IT teams handling big programming tasks on a daily basis. With a BYOD policy, companies can rely on the employees’ initiative to update their own technology and install the latest security patches for important software.
Boost in Employee Productivity and Employee Satisfaction
68% of organizations report that BYOD helped improve employee productivity. Personal and mobile devices are customized to the employee’s personal preferences, allowing them to accomplish tasks comfortably. In addition, the convenience of using a personal device saves precious time; employees can bring their work wherever they are. They no longer have to wait to reach the office to respond to an email or phone call.
The Risks of a BYOD Security Policy
As promising as BYOD is in promoting productivity, challenges in safeguarding corporate data are a pressing concern for many companies. BYOD requires the IT department to assert mobile device management and outline well-defined BYOD policies.
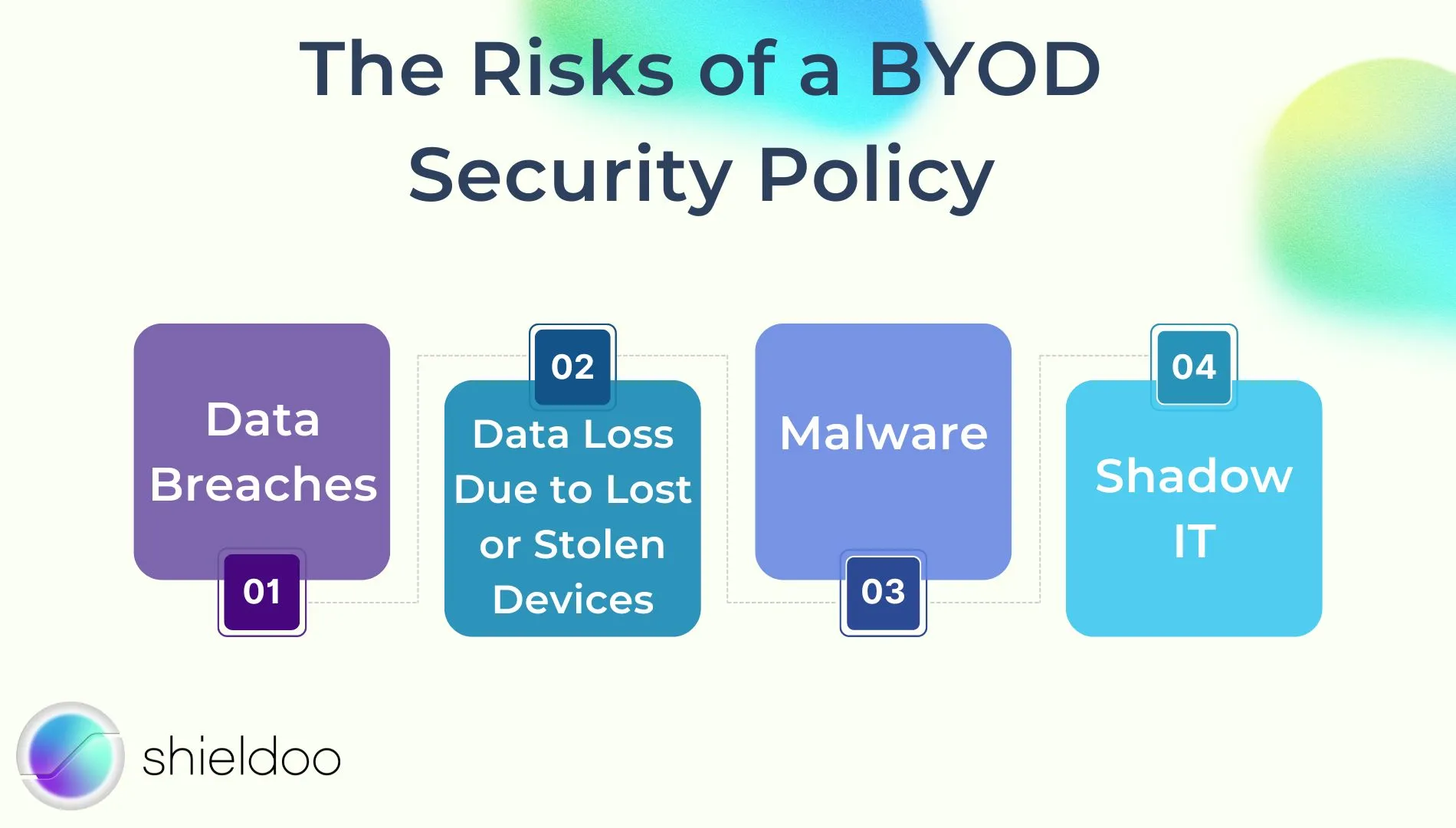
Data Breaches
The threat to information security holds back 30% of organizations from adopting BYOD in the workplace. Should the employee’s personal accounts be compromised, personal information, as well as critical company data and client information may fall into wrong hands.
Data Loss Due to Lost or Stolen Devices
If an employee loses or gets their device stolen, they also risk the confidentiality of company information. Without proper BYOD security solutions, hackers can infiltrate company networks and compromise the safety and privacy of client data.
Malware
BYOD combines personal and work accounts on a device; if an employee is not careful with their activities, they may compromise device health and the security of company information with malware attacks. For instance, PDF reader programs and games may carry malware that infects the device and infiltrates the company’s database the next time the employee logs in.
Shadow IT
32% of employees working in a remote setup use third-party services without the approval of the IT department. While these software programs help employees streamline their daily tasks, they do not meet the company’s security standards. As harmless as these applications appear, their security infrastructures are vulnerable to cyberattacks, leaving the company network vulnerable to the malicious intent of cybercriminals.
Best Practices in Adopting BYOD Security
BYOD promotes greater productivity and employee mobility but, at the same time, brings light to various security concerns. With proper mobile device management and security measures, risks and vulnerabilities can be mitigated to make the most out of the employees’ personal devices.
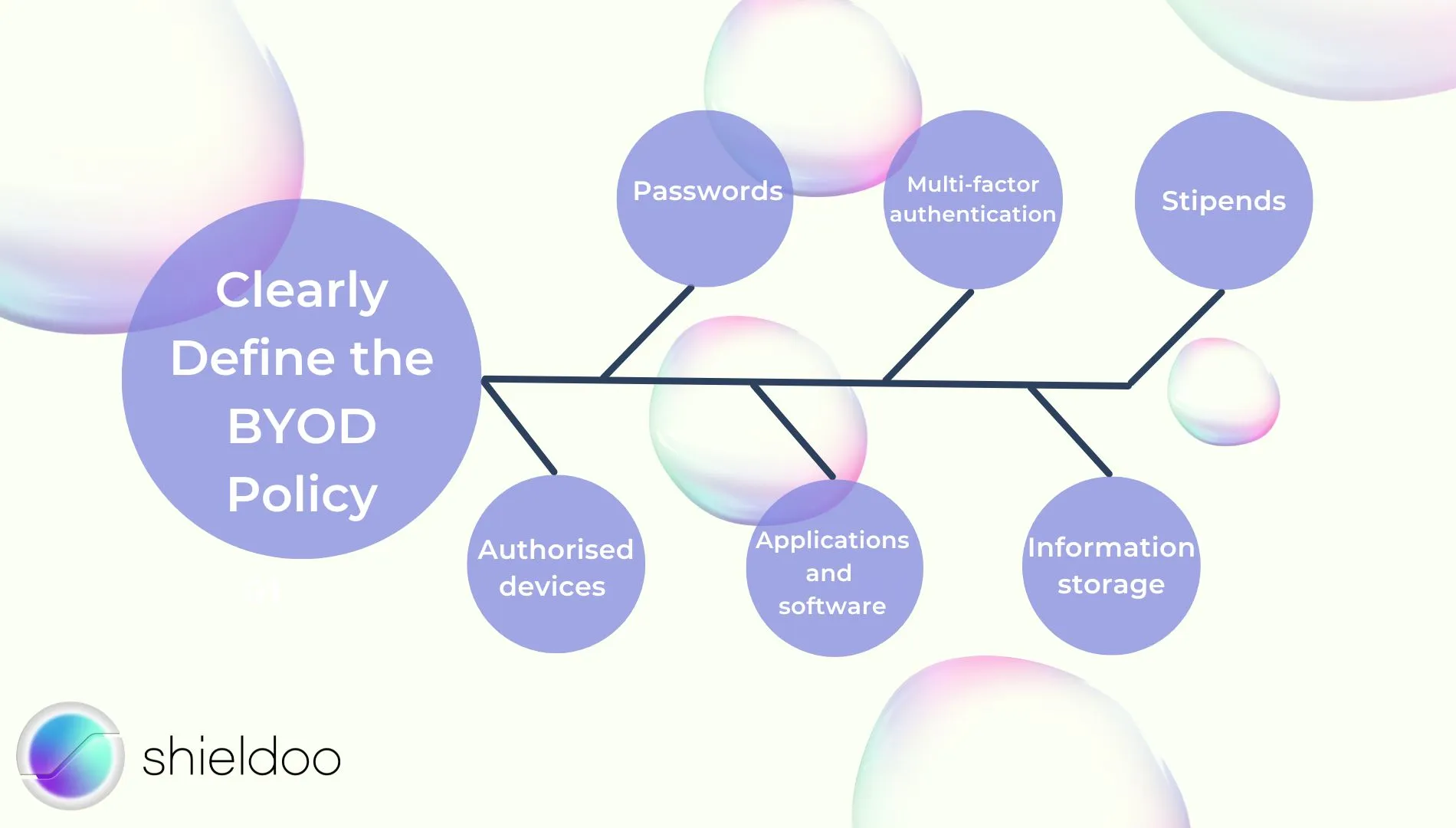
Clearly Define the BYOD Policy
Practicing BYOD requires a company to highlight guidelines, specifications, and other necessary provisions for employees to use their own devices for work comfortably. A well-established BYOD policy is easy to read and understand so employees of varying ranks can comply accordingly.
What operating systems are the minimum requirement for a smooth working experience? Can an employee use multiple devices? What are the risks and liabilities of using personal devices for work purposes? The BYOD policy must encompass the essential elements for employees in all departments, outlining every disclaimer and company right to uphold a successful BYOD practice.
Consider the following elements in writing up a BYOD policy:
- Passwords – Define password strength to secure sensitive data
- Multi-factor authentication – Reinforce account credentials and login attempts
- Stipends– Allocate a stipend to cover the cost of resources consumed as employees use personal devices for work-related purposes
- Authorized devices – Define the number and device specifications an employee is entitled to use
- Applications and software – Define company rights to ban the installation of certain software as a prevention of malware attacks
- Information storage – Define what and how much corporate data an employee can store locally on their device
Educate Employees on Cybersecurity
Acknowledging BYOD security risks and the vulnerabilities it poses for the company is also crucial for employees to work efficiently with their own devices. Invest time in training sessions and seminars to provide employees with the necessary skills and tools to keep corporate data protected while working from the comfort of their home or private office spaces.
Implement Security Measures
Implementing security measures is vital in keeping the safety of corporate networks and client data from malicious people on the Internet. While every employee is busy accomplishing work on their own device, the company still has the authority to establish security protocols.
For instance, organizations can list names of trusted software for employees to use in accessing work documents. Another example would be requiring employees to connect to a virtual private network (VPN) whenever they are accessing the corporate network from a remote location.
Establish Mobile Device Management
Security breaches are not limited to an employee’s time of employment. When a previous employee’s account is still accessible, the company is vulnerable to data loss and leakage. Establish a mobile device management strategy to monitor account credentials and user access privileges. Mobile device management services are available on the cloud so IT and HR representatives can control, restrict, and revoke user access rights when an employee leaves the organization.
Promote Efficiency at the Workplace with the Ideal BYOD Policy
Staying aware of the risks of BYOD is the first step in developing the ideal BYOD policy. Drawbacks and vulnerabilities will persist, but with the right security measures in place, any company can embrace BYOD and improve overall performance.
A good BYOD policy upholds the safety and privacy of corporate networks. Collaborate with department heads in your company to determine the level of authority and ownership the company can exercise over personally owned devices. Strategize a good device management strategy to monitor employee activity on corporate networks and encrypt sensitive information.
Reinforce account security wherever, whenever with Shieldoo™️, a cloud-based secure network developed to provide peer-to-peer data encryption. Boost your BYOD policy with Shieldoo™️’s feature-rich security functions such as multi-factor authentication, zero-trust network access, and single sign-on.

Strengthen BYOD Security With Shieldoo™️
As employee-owned devices set the new norm for accomplishing work in-office and remotely, acquiring reliable security infrastructure is a top priority. Shieldoo™️ is an excellent network to protect business networks and sensitive data from the prying eyes of the public internet. It isa peer-to-peer networking tool based off Nebula – every device signing into the network is configured and verified prior to granting network access.
In addition, Shieldoo™️ grants time-limited access. This ensures devices, whether corporate or employee-owned, only gain temporary access. When access certificates expire, users no longer have access to the network, mitigating the risk of data leakage and internal breaches.
Finally, Shieldoo™️ safeguards company networks and user accounts with zero trust. Regardless of the device, geographical location, and role, all users must verify their identities and intent in requesting access to files or applications stored in the network.
Shieldoo™️ is a lightweight, yet robust, security solution for companies and business users to leverage their BYOD policies.
FAQs
What is an example of BYOD?
Bring your own device (BYOD) is the practice of using personal and mobile devices for work. Laptops, smartphones, and tablets are some of the popular devices employees bring to work to aid them in their daily tasks.
What are the advantages of BYOD?
BYOD helps organizations save money and other resources on acquiring equipment for all employees. Personal devices are also more convenient for employees to use as they can access both work and personal matters on the same device. In addition, upgrading to the latest version or patch update for operating systems and software is more manageable – the IT department can leave it up to the employee’s initiative to update their software, saving precious time in running software updates and maintenance checks for multiple company-issued devices.
What are the challenges with BYOD?
BYOD encourages employees to use their own devices in accomplishing work. Without proper security protocols in place, this poses several risks and vulnerabilities to the security of the corporate network and other sensitive information. Challenges in adopting BYOD include: operating system vulnerabilities due to different device models and generations, information security threats, data breaches, lost and stolen devices, malware attacks, shadow IT...
What should a BYOD policy include?
BYOD policies should inform employees of the dos and don’ts of practicing BYOD while upholding the safety of company information and networks. A good BYOD policy should highlight device specifications and requirements, IT support, user access, and data ownership.
Which companies can adopt BYOD?
Businesses and organizations of all sizes – from emerging startups to large-scale corporations – can adopt BYOD with the right security solutions. Companies with a remote or hybrid work setup maximize the benefits of BYOD.





